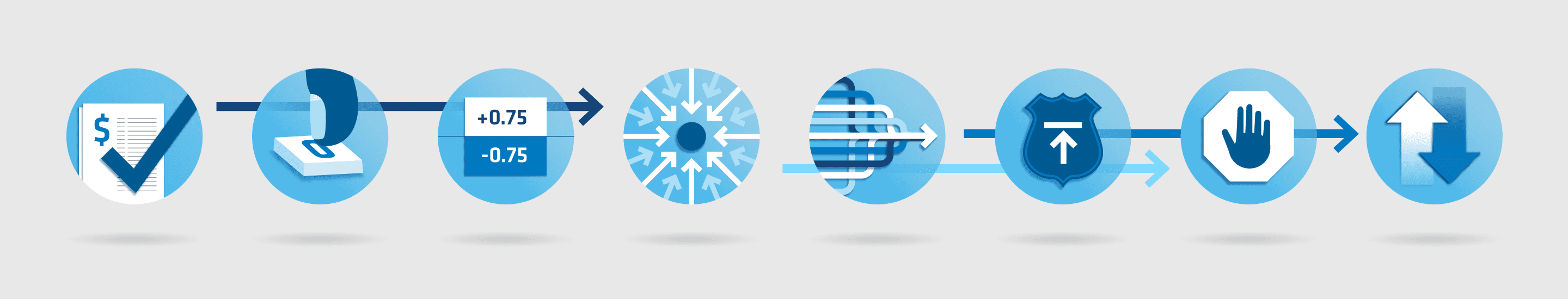
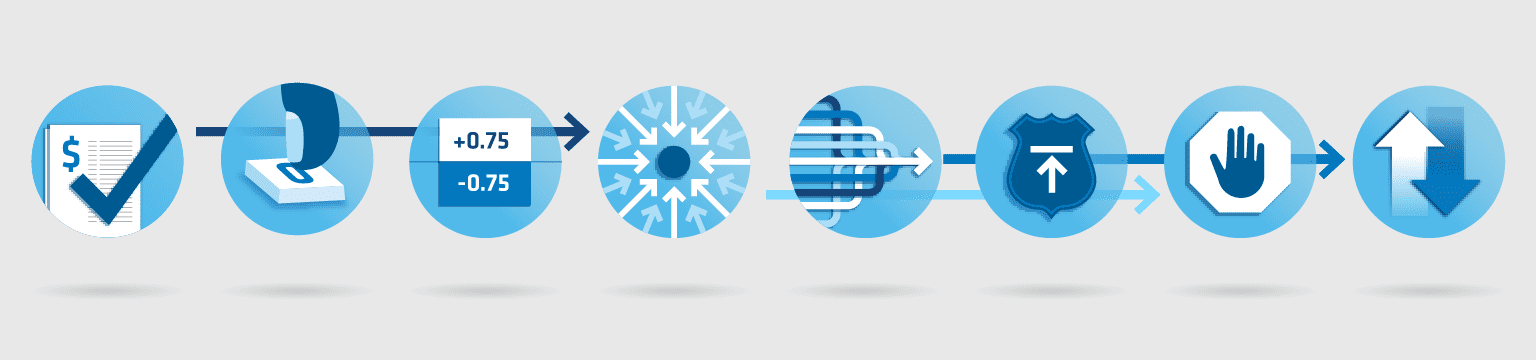
Clearing involves a number of protections that take place instantaneously from the time an order is placed to the time it is settled. And by enabling traders to submit their orders through a central clearing function, the process enables the market to run more smoothly and efficiently.
The market protections of an electronic trade
Futures exchanges process millions of trades each day. With so many orders coming at once, you need a lot of checkpoints to make sure everything goes smoothly.
Here’s a look at a few of the risk protections that every order must pass in order to make it through an electronic trading engine. These protections help maintain the integrity of the overall futures market.
The Journey
Protecting the market
Let’s take a look at just a few of the protections a single electronic trade must pass.
Credit Controls
Clearing firms set credit limits based on order size or risk values. If specified limits are breached, the order is rejected.
Maximum order quantity
Every product has a pre-defined maximum quantity per order. This step ensures that the order is not exceeding this limit before it continues. If the max quantity is exceeded, the order is rejected.
Price banding
All orders on an electronic trading platform are subject to price verification. Bids at prices well above or well below the market fall outside of that contract’s “band” and are rejected.
Central limit order book
The exchange operates a unified central limit order book because all orders from the member firms are routed to and executed on the exchange’s own trading platform. This single, integrated market allows for concentrated liquidity in one transparent location. An order is accepted once it meets the previous protection standards.
Simultaneous protections
The entire clearing process for our trade will take about 1 millisecond. (To understand just how fast that is, consider that one blink of a human eye takes about 300 milliseconds.) So it’s no wonder that, at this point, everything starts happening at the same time.
Single market data feed
Once an order is received, it's sent to the central limit order book where it’s made available to be bought or sold. From the order book, all market participants receive the market data they need to make trading decisions.
Market & stop order protection points
Every market or stop order is assigned a price limit. Customers have two options when placing these orders: assign a price limit within price bands or let a matching engine assign one.
Stop price logic
Order matching is paused when cascading stop orders cause the market to move beyond a pre-determined range. This step restores balance to the market.
Velocity logic
Regardless of order type, order matching is paused when prices move excessively and too quickly. Like stop price logic, this step keeps the market balanced.
Trade complete!
The trade makes its way through the matching engine, and our trade is completed. The contracts are now ours. If we decide to sell them back into the market, we know it will be secure and balanced thanks to all the protections we just explored.